

基于Google Earth Engine的前郭县春季农田覆膜提取
|
邓韵谣(1999—),女,黑龙江牡丹江人,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤退化过程的模型模拟分析。E-mail: dengyunyao@stu.hrbnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-05-01
修回日期: 2023-09-20
网络出版日期: 2024-08-29
基金资助
国家重点研发计划项目(2021YFD1500105)
吉林省自然科学基金项目(YDZJ202201ZYTS550)
版权
Extraction of spring farmland plastic mulching in Qianguo County based on Google Earth Engine
Received date: 2023-05-01
Revised date: 2023-09-20
Online published: 2024-08-29
Supported by
National Key R&D Plan Project(2021YFD1500105)
Jilin Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project(YDZJ202201ZYTS550)
Copyright
本文基于Google Earth Engine(GEE)云平台,综合考虑光学影像的波段反射率、光谱指数特征和雷达影像的极化、纹理特征,分别构建仅使用光学特征、仅使用雷达特征以及光学和雷达特征组合3种特征输入组合;根据精度确定最佳输入特征后,分别结合机器学习中的分类与回归树、支持向量机、最小距离分类法、梯度提升树和随机森林5种方法建立覆膜提取模型,依据结果精度评估不同方法的性能,并基于最优化模型提取出最终的覆膜农田面积。结果表明:① 最佳输入特征为波段反射率特征+光谱指数特征+极化特征+纹理特征;② 采用随机森林方法建立的模型精度最高,研究区I的总体精度达到了95.84%,Kappa系数为0.95,地物错分率为1.2% ,明显优于其他4种方法(地物错分率较分类与回归树、支持向量机、最小距离和梯度提升树法降低0.8%、7.3%、38.0%和0.3%),研究区II的验证精度达到了87.84%,证明该模型在覆膜提取中可以取得更加准确的结果;③ 使用本文方法得到2022年研究区I覆膜农田面积为1 302.48 km2,估算地膜使用量约为
邓韵谣 , 李晓洁 , 任建华 . 基于Google Earth Engine的前郭县春季农田覆膜提取[J]. 地理科学, 2024 , 44(8) : 1417 -1425 . DOI: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.20230651
Based on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) cloud platform, this paper comprehensively considers the band reflectivity and spectral index characteristics of optical images and the polarization and texture characteristics of radar images, and constructs three feature input combinations: Using only optical features, only radar features, and a combination of optical and radar features. After determining the best input features based on accuracy, this paper combines five machine learning methods, namely classification and regression tree, support vector machine, minimum distance, gradient boosting decision tree, and random forest, to establish a plastic mulching extraction model. The performance of different methods is evaluated based on the accuracy of the results, and the final plastic mulching area is extracted based on the optimization model. The results show that: 1) The combined optical and radar image characteristics have the highest accuracy in extracting plastic mulching coverage, and the optimal input features are band reflectivity features + spectral index features + polarization features + texture features; 2) The model established using the random forest method has the highest accuracy. The overall accuracy of study area I reached 95.84%, the Kappa coefficient was 0.95, and the ground object misclassification rate was 1.2%, which was significantly better than the other four methods (the ground object misclassification rate was 0.8%, 7.3%, 38.0% and 0.3% lower than that of classification and regression tree, support vector machine, minimum distance and gradient boosting decision tree method), and the verification accuracy of study area II reached 87.84%, proving that the model can obtain more accurate results in plastic mulching extraction; 3) Using the method in this paper, the area of plastic mulching farmland in study area I in 2022 is
表1 覆膜提取模型中光学及雷达影像特征集Table 1 Feature sets of optical and radar images in the farmland plastic mulching extraction model |
| 光学特征 | 变量 | 雷达特征 | 变量 | |
| 反射率特征 | B1,B2,B3,B4,B5,B6,B7,B8,B8A,B9,B11,B12 | 纹理特征 | Contrast,ASM,Correlation,Variance,Entropy,IDM | |
| 光谱指数特征 | NDVI、EVI、SAVI、RRI、NDWI | 极化特征 | VV,VH |
表2 覆膜提取模型中不同输入特征及机器学习方法分类精度Table 2 Classification accuracy of different input features and machine learning methods |
| 特征组合 | 分类方法 | 错分率/% | 各地物分类精度 | |||||||
| 覆膜/% | 旱地/% | 水田/% | 道路/% | 林地/% | 居民地/% | 水体/% | 未利用地/% | |||
| 光学特征 | CART | 2.8 | 94.6 | 96.3 | 99.9 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 89.3 | 99.8 | 98.0 |
| SVM | 14.4 | 74.5 | 88.8 | 99.3 | 90.4 | 98.4 | 67.0 | 95.0 | 71.2 | |
| 最小距离 | 23.9 | 56.0 | 67.8 | 94.3 | 89.0 | 88.0 | 50.0 | 96.3 | 67.8 | |
| GBDT | 2.8 | 96.4 | 95.5 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 87.6 | 99.4 | 97.0 | |
| RF | 3.0 | 96.3 | 95.8 | 99.9 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 86.3 | 99.8 | 98.6 | |
| 雷达特征 | CART | 4.2 | 92.0 | 88.2 | 99.8 | 98.6 | 99.8 | 96.0 | 99.4 | 93.0 |
| SVM | 26.2 | 69.5 | 59.6 | 97.3 | 45.4 | 94.0 | 82.0 | 99.6 | 43.0 | |
| 最小距离 | 39.4 | 42.2 | 31.8 | 79.0 | 59.0 | 42.0 | 57.6 | 92.6 | 80.4 | |
| GBDT | 4.6 | 93.2 | 88.2 | 99.6 | 97.8 | 99.2 | 93.6 | 99.2 | 92.8 | |
| RF | 3.8 | 93.8 | 90.9 | 99.7 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 96.6 | 99.6 | 90.6 | |
| 联合光学与 雷达特征 | CART | 2.0 | 97.2 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 95.3 | 99.4 | 96.6 |
| SVM | 8.5 | 76.3 | 91.1 | 99.7 | 90.0 | 99.6 | 96.0 | 99.6 | 79.6 | |
| 最小距离 | 39.2 | 45.2 | 28.1 | 78.1 | 59.0 | 42.1 | 55.6 | 92.8 | 85.5 | |
| GBDT | 1.5 | 97.0 | 97.6 | 100.0 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 97.0 | 99.6 | 97.6 | |
| RF | 1.2 | 97.6 | 97.6 | 99.9 | 100.0 | 99.8 | 97.6 | 99.8 | 98.4 | |
附表1 不同方案分类结果与Sentinel-2真彩色合成影像对比Appendix Table 1 The classification results of different schemes are compared with Sentinel-2 true color synthetic images |
| 机器学习算法 | 组合 | 分类结果 |
| 注:a. 光学特征;b. 雷达特征;c. 光学+雷达特征;数字1~6分别表示典型放大区内分类结果与Sentinel-2真彩色合成影像上的对比情况。 | ||
| CART | a | 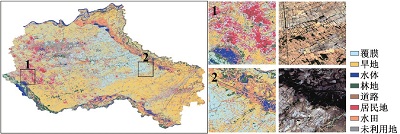 |
| b | 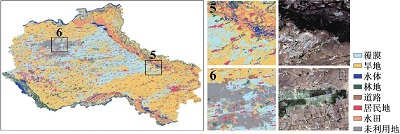 | |
| c | 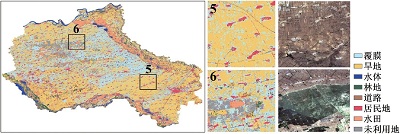 | |
| SVM | a | 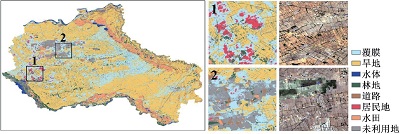 |
| b | 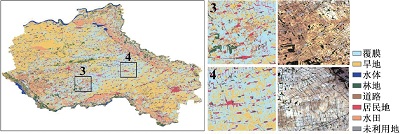 | |
| c | 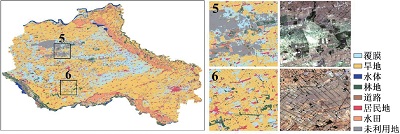 | |
| 最小距离 | a | 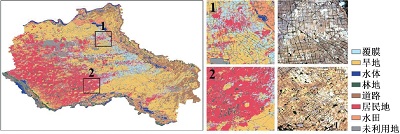 |
| b |  | |
| c | 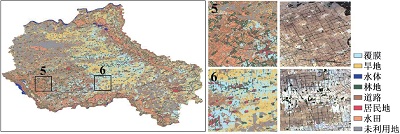 | |
| GBDT | a | 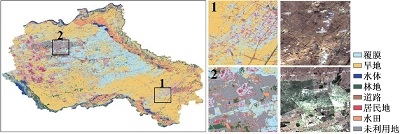 |
| b |  | |
| c | 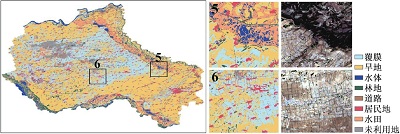 | |
| RF | a | 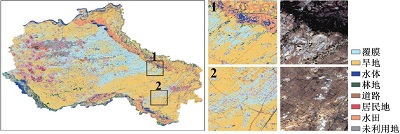 |
| b | 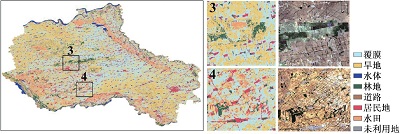 | |
| c | 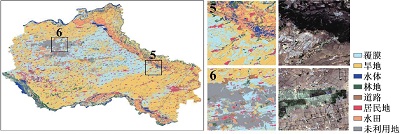 | |
| [1] |
杜建斌. 旱灾对我国粮食主产省粮食产量的影响及抗旱对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021
Du Jianbin. Study on the effects of drought on grain yield in China’s main grain-producing province and the countermeasures against drought. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
|
| [2] |
国家统计局, 环境保护部. 2015中国环境统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015
National Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Environmental Protection. 2015 China environmental statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2015.
|
| [3] |
严昌荣, 刘恩科, 舒帆, 等. 我国地膜覆盖和残留污染特点与防控技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(2): 95-102.
Yan Changrong, Liu Enke, Shu Fan et al. Characteristics and prevention and control technology of plastic film mulching and residual pollution in China. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(2): 95-102.
|
| [4] |
丁凡, 李诗彤, 王展等. 塑料和可降解地膜的残留与降解及对土壤健康的影响: 进展与思考[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2021, 8(3): 83-89.
Ding Fan, Li Shitong, Wang Zhan et al. Residue and degradation of plastics and degradable mulch and its impact on soil health: Advances and considerations. Journal of Hunan Ecological Sciences, 2021, 8(3): 83-89.
|
| [5] |
薛宇飞. 基于Sentinel-2数据的梁河县烟草区域遥感监测与分析研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2022
Xue Yufei. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis of tobacco areas in Lianghe County based on Sentinel-2 data. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2022.
|
| [6] |
Eufemia Tarantino, Benedetto Figorito. Mapping rural areas with widespread plastic covered vineyards using true color aerial data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(7): 1913-1928.
|
| [7] |
Hasituya, Chen Zhongxin, Wang Limin et al. Monitoring plastic-mulched farmland by Landsat-8 OLI imagery using spectral and textural features[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(4): 353.
|
| [8] |
Lu Lizhen, Di Liping, Ye Yanmei et al. A decision-tree classifier for extracting transparent plastic-mulched landcover from Landsat-5 TM Images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(11): 4548-4558.
|
| [9] |
Hao Pengyu, Chen Zhongxin, Tang Huajun et al. New workflow of plastic-mulched farmland mapping using multi-temporal Sentinel-2 data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(11): 1353.
|
| [10] |
Liu Changan, Chen Zhongxin, Wang Di et al. Assessment of the X- and C-band polarimetric SAR data for plastic-mulched farmland classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(6): 660.
|
| [11] |
张俊尧, 尹华. 扶余市水资源开发利用存在问题及其节水潜力分析[J]. 农业与技术, 2015, 35(23): 54-55+69
Zhang Janyao, Yin Hua. Analysis of the problems in water resources development and utilization and their water-saving potential. Agriculture and Technology. 2015, 35(23): 54-55+69.
|
| [12] |
李英, 刘艳辉, 贾顺. 扶余市花生生产现状及发展对策[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020(777): 56-58.
Li Ying, Liu Yanhui, Jia Shun. Peanut production status and development countermeasures in Fuyu City. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(777): 56-58.
|
| [13] |
国家统计局.12-6各地区农用塑料薄膜和农药使用量情况(2014)[M/OL]. 2016-09-19. http://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/ztsj/hjtjzl/2014/202303/t20230303_1923993.html
National Bureau of Statistics.12-6 Use of agricultural plastic film and pesticides in each region (2014).2016-09-19.http://www.stats.gov.cn/zt_18555/ztsj/hjtjzl/2014/202303/t20230303_1923993.html.
|
| [14] |
黄翀, 许照鑫, 张晨晨, 等. 基于Sentinel-1数据时序特征的热带地区水稻种植结构提取方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(09): 177-184.
Huang Chong, Xu Zhaoxin, Zhang Chenchen et al. Extraction of rice planting structure in tropical regions based on temporal characteristics of Sentinel-1 data. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(09): 177-184.
|
| [15] |
赵峰, 张雷昕, 王腾, 等. 城市地表形变的双极化Sentinel-1数据极化时序InSAR技术监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(9): 1507-1514.
Zhao Feng, Zhang Xin, Wang Teng et al. Bipolarization Sentinel-1 data of urban surface deformation. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(9): 1507-1514.
|
| [16] |
王春玲, 樊怡琳, 庞勇, 等. 基于GEE与Sentinel-2影像的落叶针叶林提取[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2023, 45(8): 1-15.
Wang Chunling, Fan Yilin, Pang Yong et al. Extraction of deciduous coniferous forest based on GEE and Sentinel-2 images. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2023, 45(8): 1-15.
|
| [17] |
Zhou Zhigao, Lin Aiwen, He Lijie et al. Evaluation of various tree-based ensemble models for estimating solar energy resource potential in different climatic zones of China[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(9): 3463.
|
| [18] |
马小茗, 李瑞平, 李鑫磊, 等. 河套灌区地下水埋深与土壤盐分对增强型植被指数的联合影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2023, 41(3): 134-141+165.
Ma Xiaoming, Li Ruiping, Li Xinlei et al. Combined influence of groundwater burial depth and soil salinity on enhanced vegetation index in Hetao irrigation area. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2023, 41(3): 134-141+165.
|
| [19] |
Zhen Zhijun, Chen Shengbo, Yin Tiangang et al. Using the negative soil adjustment factor of soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) to resist saturation effects and estimate leaf area index (LAI) in dense vegetation areas[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(6): 2115-2115.
|
| [20] |
Li Mengmeng, Bijker Wietske. Vegetable classification in Indonesia using Dynamic Time Warping of Sentinel-1A dual polarization SAR time series[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation, 2018, 78: 268-280.
|
| [21] |
张征云, 江文渊, 张彦敏, 等. 基于哨兵SAR数据和多光谱数据的水稻识别研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(4): 556-564.
Zhang Zhengyun, Jiang Wenyuan, Zhang Yanmin et al. Rice identification study based on sentinel SAR data and multispectral data. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2023, 39(4): 556-564.
|
| [22] |
赵悦. 基于不同裂纹特征的苏打盐碱土EC预测能力的对比研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2023
Zhao Yue. Comparative study on the EC prediction ability of baking soda saline soil based on different crack characteristics. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2023.
|
| [23] |
党涛, 李亚妮, 罗军凯, 等. 基于最小距离法的面向对象遥感影像分类[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2017, 40(10): 163-165+169+173.
Dang Tao, Li Yani, Luo Junkai et al. Object-oriented remote sensing image classification based on the minimum distance method. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2017, 40(10): 163-165+169+173.
|
| [24] |
陈果, 李乐林, 陈浩, 等. 多特征优选的Sentinel-2A影像随机森林分类研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2023, 46(3): 19-23.
Chen Guo, Li Lelin, Chen Hao et al. Multi-feature preferred Sentinel-2A image random forest classification study. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2023, 46(3): 19-23.
|
| [25] |
贾煜. 基于Sentinel-2数据的喀斯特典型地区土地覆盖分类研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2022
Jia Yu. Land cover classification study of typical karst areas based on Sentinel-2 data. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022.
|
| [26] |
Guillaume R, Marc D, Konrad S et al. Assessment of deep learning techniques for land use land cover classification in Southern New Caledonia[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(12): 2257.
|
| [27] |
元文. 怎样计算地膜的用量[J]. 中国农村小康科技, 2003(4): 36.
Yuan Wen. How to calculate the amount of mulch film. China’s Rural Well-off Science and Technology, 2003(4): 36.
|
| [28] |
王利花, 金辉虎, 王晨丞, 等. 基于合成孔径雷达的农作物后向散射特性及纹理信息分析——以吉林省农安县为例[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(9): 1385-1393.
Wang Lihua, Jin Huihu, Wang Chencheng et al. Analysis of backscatter characteristics and texture information of crops based on synthetic aperture radar — Take Nong’an County, Jilin Province as an example. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(9): 1385-1393.
|
| [29] |
张萍萍, 申双和, 李秉柏, 等. 水稻极化散射特征分析及稻田分类方法研究[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2006(1): 148-152.
Zhang Pingping, Shen Shuanghe, Li Bingbo et al. Analysis of polarized scattering characteristics and classification method of rice field. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2006(1): 148-152.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |